Traceability. Understand the Relationships between Artefacts.
What is traceability good for and what sorts of traceability are there?
Traceability concerns the comprehension of relationships between artefacts and development processes. According to ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765:2010, traceability is: 'Discernable association among two or more logical entities, such as requirements, system elements, verifications and tasks.'
The Guide to Business Analysis Body of Knowledge BABOK v3 defines Requirements Traceability as: 'The ability for tracking the relationships between sets of requirements and designs from the original stakeholder need to the actual implemented solution.'
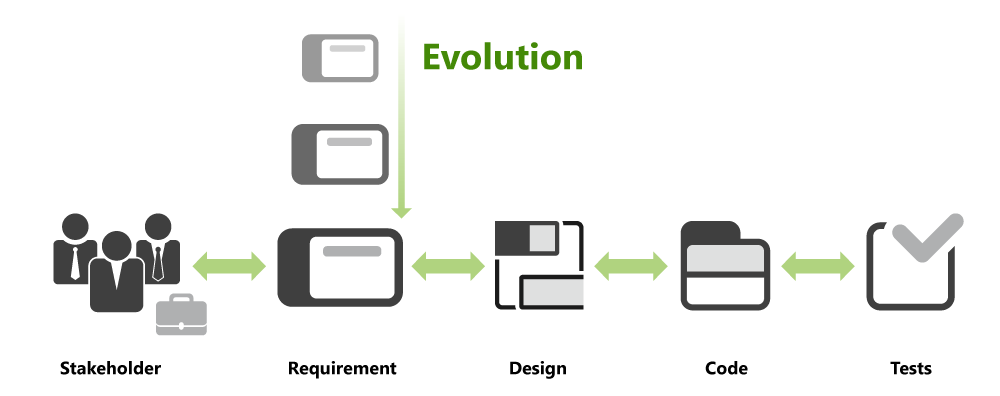
The relationships between requirements and their sources - the stakeholders with their need - can be understood in both directions. This type of traceability is known as Pre-Requirements Traceability.
The relationships between requirements, the draft, the code and the tests can be followed in two directions. This is known as Post-Requirements Traceability.
Answer many questions with objectiF RPM: To whom and how is a requirement important? Has a requirement already been changed? What do all the changes of a requirement concern? Are test cases still lacking?
Traceability – Some Definitions
When talking about Traceability, three concepts are often blended together that are closely related:
- Revision security concerns the tracing back of the history of artefacts that emerge in the development process. It is strongly anchored in the process standards like, for example, the German V-Modell XT or other waterfall models. To create revision security is a theme for the version and configuration management.
- Compliance is understood at the traceability of the compliance of processes and standards. In regulated industries like the automotive sector, compliance is a central aspect and a prerequisite, for example, for a successful Automotive SPICE Assessment.
- Traceability describes the comprehension of the relationships between artefacts of the development process.
According to ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765:2010, traceability is the ‘Discernable association among two or more logical entities, such as requirements, system elements, verifications and tasks.’ The Guide to Business Analysis Body of Knowledge BABOK v3 concretes this definition for the special case of Requirements Traceability: ‘The ability for tracking the relationships between sets of requirements and designs from the original stakeholder need to the actual implemented solution.’
Traceability creates an understanding of the relationship of artefacts of the development process. That is how it differs from revision security and compliance.
Pre and Post-Requirements Traceability
According to BABOK v3, the relationship between requirements and their source – the stakeholders with their needs – should be able to be understood in both directions. This type of traceability is known as Pre-Requirements Traceability. Likewise, the relationships between requirements, the draft, code and the tests should be able to be followed in both directions. This is referred to as Post-Requirements Traceability. Both forms of requirements traceability help answer the many questions that emerge over the course of the development process.
- Examples of questions of pre-requirements traceability: to whom is the requirement important, and how? How will the need be met?
- Examples of questions of post-requirements traceability: has a requirement been changed? What is effected by the changes to the requirement? Are artefacts like test cases lacking?
Requirements-To-Task Traceability
Pre and post-requirements traceability are not the only forms of traceability, because changes happen not just with other requirements, but also between those that are already related. That is how BABOK v3 differentiates between business, stakeholder and solution requirements that derive from each other. Apart from that, requirements come in requirement and specification documents like specification sheets or the Software Requirements Specification of the IEEE. The traceability of the relationships of the requirements amongst themselves and to the documentation is known as Inner Traceability.
Example of a question of inner traceability: Which requirements and requirement documents are affected by changes to a requirement?
Requirements-To-Task Traceability
Requirements are realized in the course of development. That is how relationships emerge between requirements and tasks in project planning. With the help of these relationships, the development of requirements is comprehensible.This form of traceability is known as Requirements-to-Task Traceability.
Example of questions of requirements-to-task traceability:
- What is the state of the realization?
- How much effort do the requirements put in the realization?
- Who realized the requirement?
What Is Traceability Good for?
The different forms of requirements traceability support four analysis steps:
- Effect analysis – Which requirements/artefacts will be influenced by changes?
- Origin analysis – Why is this requirement/artefact there?
- Coverage analysis – Are all requirements/artefacts taken into account for a full solution?
- Performance value analysis – how is the work proceeding?
Traceability moves you into the position to answer the diverse questions in your development: Which requirements are influenced by which changes? Why is this requirement here? Are all requirements/artefacts taken into account for a full solution? How is the project proceeding? If you recognize the effects of changes, you can plan more safely and recongize risks earlier. Your maintenance efforts are easier to guess, the advancement control simplified. The traceability of requirements to your stakeholder helps validate requirements and to have pelased stakeholders. And the traceability of decisions and solutions is a prerequesite for successful audits.
The Traceablity Matrix
There are different ways to produce traceability. One possibility is the explicit documentation of the relationships between requirements themselves and other development artefacts through the creation and maintenance of a traceability matrix. There are many different MS Excel traceability templates online. Anyone who has tried to manually maintain a traceability matrix for a project, from the needs of the stakeholders to the tests, probably understands the following assessment: “A Requirements Traceability Matrix is probably one of the most valuable things people almost never do!”
Keeping a traceability matrix is time-consuming and prone to error. Even if the matrix is partially generated by a machine, there remains a high organizational and operative effort in its step-by-step completion, updating, and versioning. In practice, the approach of lean traceability asserts itself. Lean Requirements Traceability means as much traceability as necessary with as little effort as possible. You can find more information here in our Lean Traceability Whitepaper.
Traceability in the form of an explicit documentation of the relationships between requirements and to other artefacts is time-consuming and leads to more artefacts. The solution? Lean Traceability.
Traceability right of the Bat
In agile projects there can be reservations against traceability, because an explicit doumentation of the relationships between requirements and to other development artefacts leads to more artefacts. This increases expenses in that the documentation does not belong to the actual delivery scope. Agile projects become cumbersome. But there is a solution! Lean Traceability.
Completely renound the explicit documentation of traceability. Instead, manage all artefacts – stakeholders, goals, requirements, tests, documents, requirement diagrams, target diagrams and context diagrams with a single software: objectiF RPM. And if need be, generate all the information from the databank in documents. That’s how your process can stay lightweight whilst being completely comprehensible.


